Last date modified: 2026-Mar-03
aiR Assist (Advance Access)
Advance Access (AA) is an opportunity to evaluate and work with Relativity features prior to the General Availability (GA) release. Relativity customers typically participate in AA programs on a feature-by-feature basis. The functionality described in this
aiR Assist is a conversational search tool integrated within RelativityOne, designed to empower legal teams to interact with their data using natural language. By leveraging advanced AI, aiR Assist enables users to surface hidden insights, reveal connections, and uncover themes in moments directly within the Relativity platform. This transforms how legal professionals explore and understand modern legal data, leading to faster comprehension, stronger decision-making, and defensible outcomes.
It works by searching the extracted text of indexed documents. Users can create up to five indexes per workspace, each supporting up to 50,000 documents. When a query is submitted, aiR Assist identifies the most relevant documents and uses a large language model (LLM) to generate answers, complete with citations to up to 25 source documents.
See these topics to start using aiR Assist:
- Best practices (Advance Access)
- Asking a question (Advance Access)
- Indexing data using Index Manager (Advance Access)
How aiR Assist works
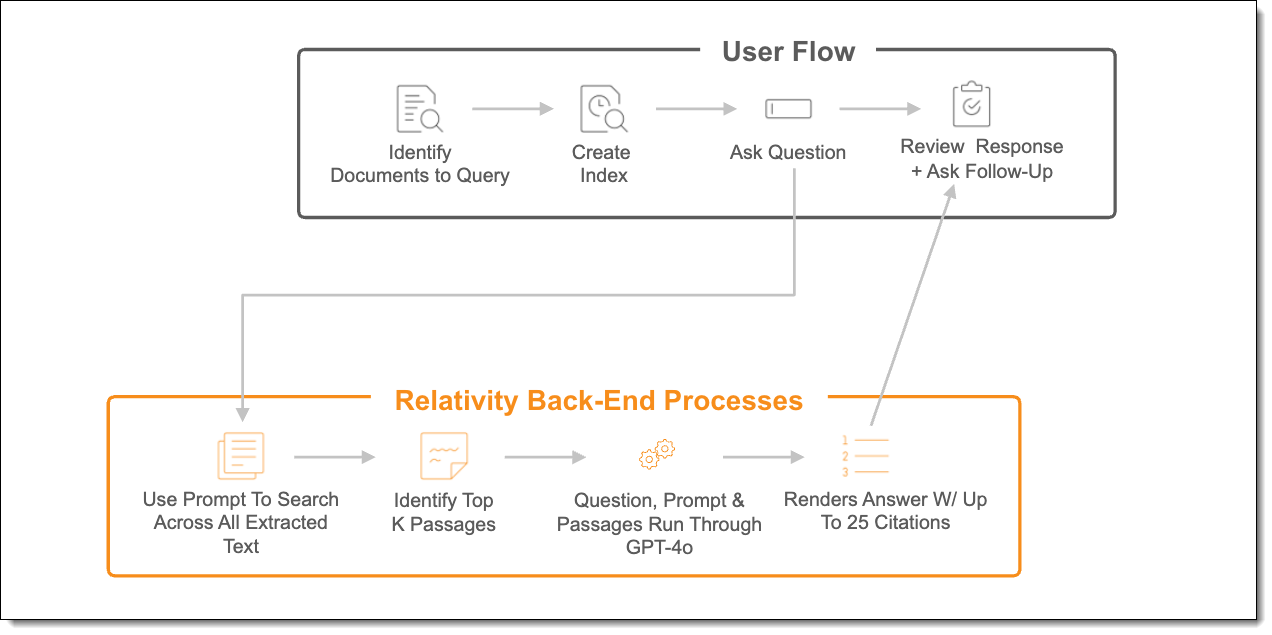
aiR Assist operates using a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) process to deliver grounded, evidence-based responses. This approach combines document retrieval with large language model generation to ensure accuracy, transparency, and contextual relevance.
- Indexing the documents (indexing step)
The user identifies documents to query and creates an index. - Asking a question (question step)
The user asks a question. - Finding relevant documents (retrieval step)
Each question is matched against the text indexed from the identified documents. aiR Assist performs a similarity search to identify the most relevant content. The documents are divided into smaller passages, and the system selects the top results that best correspond to the question. - Generating the answer (generation step)
The selected passages, along with the original question and system prompt, are passed to the LLM (GPT-4o). The model uses this retrieved context to generate a coherent, concise, and well-supported answer, including up to 25 citations and references to the original sources.
LLM model in use
aiR Assist currently uses the Open AI GPT-4o LLM, providing high-quality, contextually grounded responses supported by retrieved source material.
Important Limits
- Each index can contain up to 50,000 documents.
- A maximum of five (5) built indexes can be created per workspace.
- Individual documents must be 5 MB or smaller; larger files are excluded during indexing.
- Only documents with extracted text are indexed. The text must be stored in Data Grid (not SQL). Files that do not contain extracted text are excluded automatically from the index.
Understanding aiR Assist responses
aiR Assist is designed to identify and summarize relevant information from large document sets through natural language interaction. The system operates on a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture, which retrieves and analyzes the most relevant documents and generates a grounded response supported by citations and references.
aiR Assist focuses on returning the most contextually appropriate and evidence-based information rather than performing exhaustive or “find everything” searches. It does not review every document individually, and some occurrences of keywords or topics may not be included in the response.
The RAG process works best when key evidence is found in a few focused documents. Results are less accurate if answers depend on scattered or unclear information.
Language support
aiR Assist currently supports English-language content only. The system has been designed and tested exclusively on English-language datasets to ensure accuracy, reliability, and consistent performance.
At this time, non-English languages are not supported, and aiR Assist has not been formally evaluated or validated for use with multilingual or non-English text. While it may operate with non-English datasets, results can vary in accuracy and completeness, and verification of cited sources is strongly recommended when working with such content.
Future updates may expand language capabilities based on performance testing and model availability.
Supported use cases
Here are some example questions targeting common use cases for aiR Assist:
| Use case | Common category | Example question |
|---|---|---|
| Early Case Insight | Finding potentially important documents | Can you find me documents that discuss potential gifts or incentives? |
| Finding documents by theme | Are there any documents mentioning fraudulent behavior of John Doe? | |
| Understanding actors and roles | Who was involved in discussions about offering gifts? | |
| Case Strategy Development | Identifying a series of events | Create a high-level timeline for events that took place before the start of Project Artemis. |
| Understanding communications and relationships between actors | Who communicated with whom about the contract terms? | |
| Deposition/Trial Preparation | Suggesting exhibits based on key criteria | List documents to use as exhibits based on [key document criteria]. |
| Confirming conversations or actions took place | Did John Maxwell send an email about the compliance policy? |
Deployment and processing geographies
When using Relativity's AI technology, customer data may be processed outside of your designated geographic region. For more information, see Deployment and processing geographies.
Release notes
This section includes the release information and the current functionality of the aiR Assist (Advanced Access) application.
- Indexing Progress—new feature displaying percentage progress of indexing build or rebuild in the Docs column in Index Manager.
- Indexing Data Source—added Saved Search name to Index Description in Index Manager.
- Indexing Error List—new way of displaying additional information regarding not indexed documents including the reason why a document failed to index.
- New aiR Assist button—aiR Assist is available from the left sidebar instead of under the "Ask AI" button.
- New chat user interface—improved chat experience with the aiR Assist panel now opening on the left, while the Documents list is always in view on the right.
- Relocation of start a new chat—the start a new chat conversation option moved to the Answer a question box.
- New Index Manager—ability to filter Indexes and Data Sources (when creating an Index).
- Answer sharing—ability to copy answer to clipboard.
- Give Feedback—ability to rate an answer with Thumbs Up or Thumbs Down icons.
- Index rebuild—existing indexes can now be quickly updated to match changes in the saved search data source.
- Intent clarification—improves aiR Assist conversations by asking follow-up questions when your request is unclear, helping guide you to the right outcome and navigate the limitations.
- Saved Search Indexing—indexing documents from public saved searches is now supported.
- Multi-turn chat—simulates human conversation by preserving context from previous exchanges within the same chat session, which enables follow-up questions and deeper exploration without the need for repetition.
- Chat persistence—chat history is now saved and available for review even after user logs off their Relativity session.
- Start a new chat—this button starts a new chat conversation below the previous one, separated by a line. The new chat conversation does not reference previous conversations for its responses.
- Search Q&A button—the button is located on the top of the document list page and available for all users in the workspace to use.
- "Ask a question" box—when the panel is open, a user can input a natural language question about the documents. Each question is evaluated and answered individually without consideration of the full conversation.
- Workspace-level context—all indexed documents available in the workspace, up to 100,000, are subject to the querying process.
- Chat history—a user’s chat history is visible during that user’s Relativity session. Once the user logs out of Relativity the chat history will be cleared.
- Citations—references and citations are provided for each response. A user can filter the Document List to the show these references or can open each reference from the chat panel in the Document Viewer. Please note, that in the initial AA release, we do not confirm that the citations are grounded in the document text like in aiR for Review.







