Last date modified: 2026-Feb-05
Security Best Practices
Shared Security in RelativityOne
RelativityOne is protected by a robust security program designed to keep client data safe at every level. Relativity’s in-house security team, Calder7, attentively defends the security of RelativityOne infrastructure and data. Client System Administrators protect their RelativityOne environment by managing data access permissions, user accessibility, user authentication methods, and other instance specific security configurations.
Client Security Best Practices
To assist client System Administrators with maintaining a secure environment, the Security Configurations tab of Security Center evaluates and displays alignment with various security best practices. Each best practice focuses on a client-controlled configuration which impacts the environment’s overall security posture.
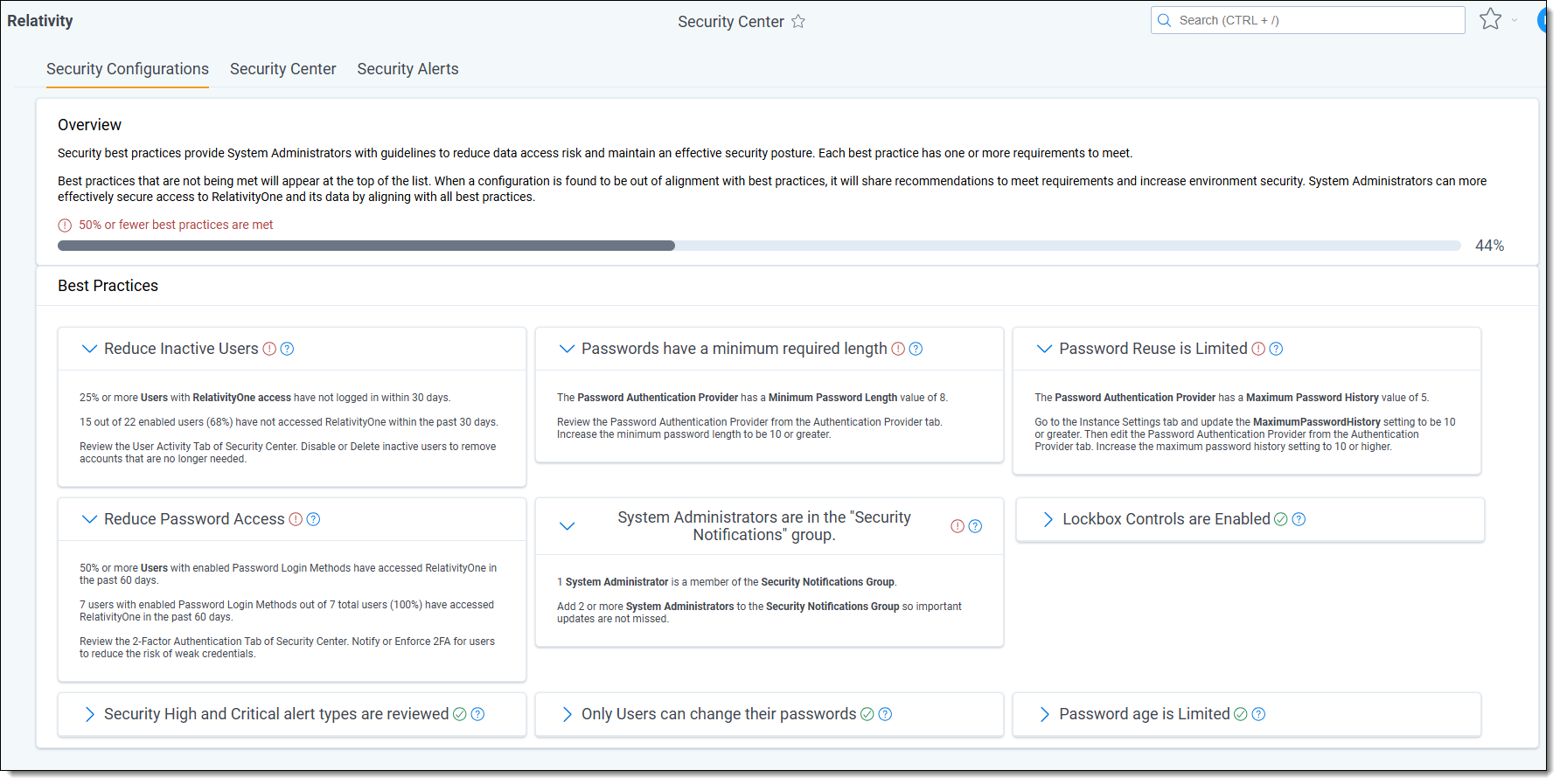
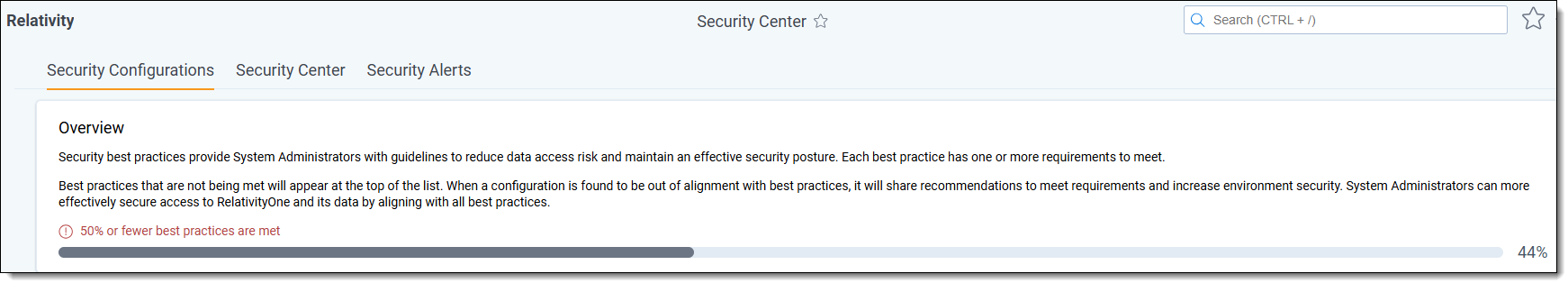
Progress towards meeting all best practices is shown at the top of the tab as a progress bar for quick assessment.
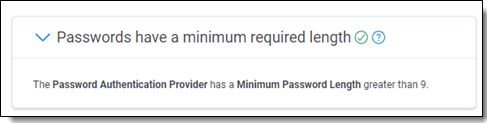
Best practice alignment is evaluated by comparing the state of configurations within RelativityOne against a secure state. Those best practices that are being met appear with a green check mark and a description of the recommendation being met.
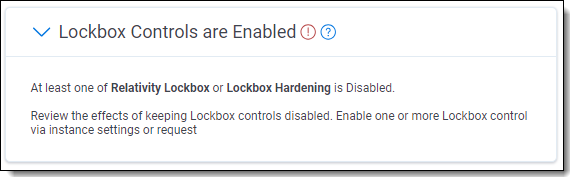
If a best practice is not being met, a message displays along with recommendations for returning to best practice alignment. The ones not met appear at the top of the list so that they can be easily identified and addressed.
List of Best Practices
Eight best practices are currently evaluated within the Security Configurations tab. Refer to the following tables for more details about each best practice, the security focus, how it is evaluated, and the recommended state to reach alignment.
Each RelativityOne security best practice represents an independent change that client System Administrators can make to better secure their environment. Meeting each best practice creates a defense in depth strategy to best protect user logins, data accessibility, and security event monitoring. Maintaining alignment with each best practice elevates RelativityOne’s security posture, security transparency, and promotes strong data accessibility controls.
User login configuration best practices:
| ID | Best Practice | Security Focus | Evaluation | Recommended Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reduce access of users with basic authentication | Users configured with basic authentication login methods have an increased risk of account compromise. | Percentage of access enabled users with an active basic authentication login method, and who have login activity within the last 30 days. | Users with basic authentication login methods are updated to have a Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) method enabled or have basic authentication replaced with another login method type. |
| 2 | Passwords have a minimum required length | Requiring longer passwords reduces the chances of successful brute force credential guessing attacks. | The Minimum Password Length value of each Password Provider type Authenticator. | Password Authenticator type login methods require passwords to be 10+ characters long. See Authentication provider settings. |
| 3 | Previous passwords cannot be reused within a secure limit | Reusing old passwords may allow attackers to compromise an account by guessing a list of previously used passwords. | The “Maximum Password History” value of each Password Provider type Authenticator. | Prevent users from reusing the last 10+ passwords. |
| 4 | The AdminsCanSetPasswords Instance Setting is False | Users should have exclusive permission to reset their passwords. | The value of the AdminsCanSetPasswords Instance Setting. | The AdminsCanSetPasswords Instance Setting is False. |
Data accessibility best practices:
| ID | Best Practice | Security Focus | Evaluation | Recommended Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Reduce the number of inactive user accounts | Inactive users may have credentials, data access permissions, and RelativityOne access that is no longer required. | Percentage of total users who have RelativityOne access and have not logged in within 30 days. | All inactive users have access disabled or are deleted if no longer needed. |
| 6 | Prevent unauthorized data access via Lockbox Controls | The Relativity Lockbox and Lockbox Hardening controls prevent Relativity employees from accessing workspaces until granted client permission. | The enabled or disabled state of Relativity Lockbox and Lockbox Hardening. | Both Relativity Lockbox and Lockbox Hardening are enabled. |
Security Alert best practices:
| ID | Best Practice | Security Focus | Evaluation | Recommended Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Security High and Critical alert types are reviewed | High and Critical level alerts are generated for important changes in data access or environment security. These events need to be reviewed with priority to ensure data remains secured. | Length of time between a High or Critical alert being created, and it being either Dismissed or Resolved. | All High and Critical alerts are resolved within 15 days of creation. |
| 8 | System Administrators are in the Security Notifications group | Security Alert and Lockbox notifications are sent to members of the Security Notifications group. System Administrators should be members to ensure these messages are received. | Number of System Administrators in the Security Notifications group. | Two or more System Administrators are in the Security Notifications group. |
1. Reduce access users with basic authentication
This best practice is evaluated by calculating the percentage of access enabled users which have an active password login method without Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) enabled. If more than 50% of users have basic authentication login methods, then the best practice is out of alignment. To bring this best practice into alignment, visit the Security Center 2-Factor Authentication tab to enable 2FA login requirements for users. Alternatively, basic authentication users can have their password login method removed and replaced with another login method type. The most secure state is for 100% of users with password logins to have 2FA enabled, or for no access enabled users to have basic authentication login methods.
2. Passwords have a minimum required length
If the minimum required length of passwords is 9 or less, then this best practice will appear out of alignment. RelativityOne System Administrators can increase the minimum password length by viewing the Authentication Provider tab, editing each “Password” type provider, and updating the “Minimum Password Length” value of each.
3. Previous passwords cannot be reused within a secure limit
RelativityOne allows System Administrators to determine how many previous passwords are blocked from reuse. The Maximum Password History setting for Password type Authentication Providers can be updated to control this. If Maximum Password History is 9 or less for any Password type Authentication Provider, then this best practice is out of alignment. System Administrators can update the setting to be 10 or more to meet the best practice. For the greatest security, Maximum Password History should be a large number to encourage never reusing a previous password.
4. The AdminsCanSetPasswords Instance Setting is False
Besides lockout type events, user account owners should be the only ones who can change their account passwords. This ensures that passwords are not known by anyone other than the owner. RelativityOne’s AdminsCanSetPasswords instance setting determines if System Administrators are allowed to modify user passwords. This best practice is met if the AdminsCanSetPasswords instance setting is False, meaning that administrators cannot change user passwords. The instance setting value can be modified in the Instance Settings tab to align with the best practice.
5. Reduce the number of inactive user accounts
Inactive users are identified as accounts which have Relativity Access enabled but have not logged in for over 30 days. These accounts may be for users who no longer need access and have not yet been removed or had permissions reduced. They pose a security risk because the accounts may still retain RelativityOne permissions that could be used for unauthorized data access. If more than 25% of all access enabled users are inactive, then this best practice is not being met. To move back into alignment, inactive users can be viewed and disabled from RelativityOne Security Center’s User Activity tab.
6. Prevent unauthorized data access via Lockbox Controls
Relativity Support team members may require access to a client’s RelativityOne environment to troubleshoot an ongoing issue. When this access occurs, the Relativity Lockbox feature prevents Support from gaining access to client workspaces. While Relativity Lockbox is enabled, Support team members are blocked from viewing client workspaces until the client grants them access. Lockbox Hardening is an additional layer of security which prevents Support from attempting to grant themselves access through updates to user accounts or group memberships. Relativity Lockbox and Lockbox Hardening are both enabled by default in RelativityOne. Both are critical to preventing unauthorized data access events. However, they can be disabled at client discretion. This best practice is met while both Relativity Lockbox and Lockbox Hardening are enabled. The current state of Lockbox controls and their impacts on data access security can be viewed in RelativityOne Security Center.
7. Security High and Critical alert types are reviewed
RelativityOne Security Alerts bring attention to changes and events impacting the security of the environment. When an alert is generated, it will appear in the Security Alerts tab along with key information about the event causing the alert. New alerts remain in the “Unresolved” state to indicate they have not yet been reviewed. System Administrators can change the alert state to either “Dismissed” to show the alert required no further action, or “Resolved” to note that a change was made to address the alert. More information about reviewing alerts is available in the RelativityOne Security Alerts documentation. Only changes that carry a substantial security risk are classified as High or Critical. This best practice is not being met if High or Critical alerts are in the “Unresolved” state for longer than 15 days. To address alerts, System Administrators can view, dismiss, and resolve alerts in the Security Alerts tab.
8. System Administrators are in the Security Notifications group
Along with appearing in the Security Alerts tab, new alerts will be sent in an email summary to members of the Security Notifications group. This group also receives notifications anytime a client grants a Relativity Support technician access to a workspace. This best practice is being met if two or more administrators are group members. Administrators can be added to the group as needed by editing the Group’s membership in the Groups tab of RelativityOne.
On this page
- Security Best Practices
- Shared Security in RelativityOne
- Client Security Best Practices
-
List of Best Practices
- 1. Reduce access users with basic authentication
- 2. Passwords have a minimum required length
- 3. Previous passwords cannot be reused within a secure limit
- 4. The AdminsCanSetPasswords Instance Setting is False
- 5. Reduce the number of inactive user accounts
- 6. Prevent unauthorized data access via Lockbox Controls
- 7. Security High and Critical alert types are reviewed
- 8. System Administrators are in the Security Notifications group







