Last date modified: 2026-Feb-05
Sampling for repeated content
Conceptual indexes benefit from targeted removal of boilerplate text, especially email confidentiality footers. Analytics offers repeated content identification, but on large document sets it can be slow and resource intensive.
This topic provides a method of running repeated content identification on random samples from a large document set. The sampling method is more efficient and uses fewer resources than running it on the full set, without sacrificing the quality of the results.
If your document set is smaller than 100,000 documents, there is no need to sample for repeated content.
See this related page:
Creating the sample
To create a sample for repeated content, perform the following steps:
- Create a random sample of the target documents.
- Navigate to the Documents tab and restrict yourself to the documents you want to focus on. It might be everything in the workspace, the searchable documents from your index, or a set limited by file type, email inclusives, or some other subset.
- Once you're looking at the document set you want to analyze, create a random sample by clicking the sampling icon (
 ).
). - In the Sampling dialog, set the following:
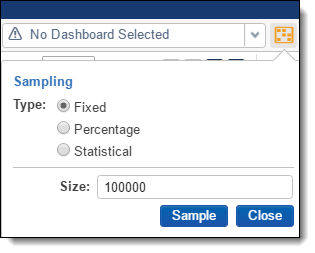
- Type: Fixed
- Size: 100,000
- Click Sample. You should now see only 100,000 documents listed on the page.
Saving sample as list and list as saved search
At this point, you're ready to create the list. From there you'll create the saved search that you'll reference in your Repeated Content Identification run.
To create the list as a mass operation:
- From the bottom of the page, click all 100,000 and then click Save as list.
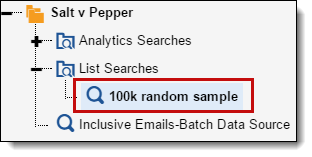
- When prompted, name the list "100k random sample".
- Navigate to the Lists tab.
- Click 100k random sample, then click Create Search from List. You should now have the 100k random sample search under the List Searches folder in your saved search browser.
Running repeated content identification as Structured Analytics set
To create a Structured Analytics Repeated Content Identification Set:
- From the Indexing and Analytics tab, select Structured Analytics Set. A list of existing Structured Analytics sets appears.
- To create a new set, click New Structured Analytics Set. The Structured Analytics Set layout appears.
- In the Structured Analytics Set Information layout, set the following:
- Name: Enter a name for your Structured Analytics set, such as "Repeated Content Identification on sample".
- Prefix: Leave as default.
- Operations to run: Repeated content identification
- Data source: select your saved search, 100k random sample.
- In the Repeated Content Identification layout, consider the following:
- You should modify the Repeated content settings slightly to suit your needs. We recommend the defaults with the exception of the Minimum number of occurrences. If you are using a random sample, we recommend you change this setting to 0.004 (i.e. 0.40%) multiplied by the number of documents you are submitting. For example, with 100,000 documents, set the Minimum number of occurrences to 400. If you are not using a sample (for instance, if you have a small collection with fewer than 100,000 documents), then we advise setting it to 0.005 times the number of documents you’re submitting. See Special considerations for more information.You may over time decide that you prefer setting this value higher or lower, but the above recommendation is consistent with our experience with most customers. Submit a ticket to Customer Support if you would like to discuss it in greater detail.
- You should modify the Repeated content settings slightly to suit your needs. We recommend the defaults with the exception of the Minimum number of occurrences. If you are using a random sample, we recommend you change this setting to 0.004 (i.e. 0.40%) multiplied by the number of documents you are submitting. For example, with 100,000 documents, set the Minimum number of occurrences to 400. If you are not using a sample (for instance, if you have a small collection with fewer than 100,000 documents), then we advise setting it to 0.005 times the number of documents you’re submitting. See Special considerations for more information.
- Click Save. The Structured Analytics Set Console appears.
- To run repeated content identification analysis, click Run, then click Run again in the pop-up options box. You can monitor the progress of the operation in a separate window by clicking the export icon in the upper right corner of the progress pane.
Review results
After the operation completes, review the resultant filters to ensure that they are indeed boilerplate and not authored content. Accomplish this task by using filters along with the Ready to index field.
Special considerations
As mentioned above, the minimum number of occurrences setting should be configured in proportion to the number of documents. While 400 is generally appropriate for 100,000 document samples, larger or smaller sets necessitate proportional modification of that number.
To retrieve more filters, the minimum number of occurrences can be reduced. However, we don't recommend setting it lower than 100 on a 100,000 document sample, as the results can become more subject to sampling error. Consider running the operation across a judgmental sample instead. For example, just parent emails, or just Word and PDF documents.







