Create a new detector
Follow the instructions below to create a new detector or tag and test regular expressions and keywords.
Create a new detector or tag
To create a new detector or tag:
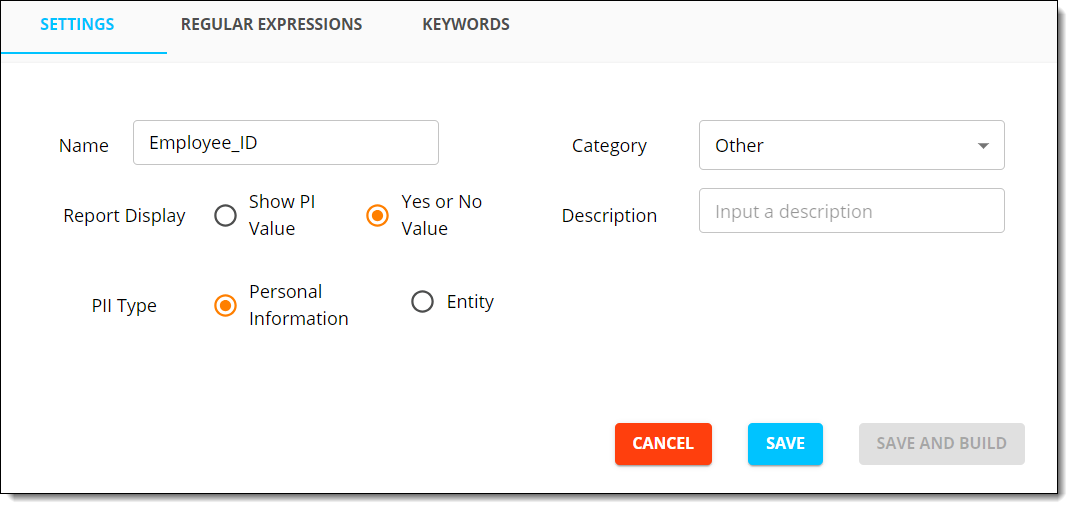
- From Project Settings, click the New button at the top left corner of the page.
- In the settings menu on the right, enter a name, description, and category for the detector and configure the PII Type.
- PII type: Whether it will be considered PI that belongs to an entity or the entity itself.
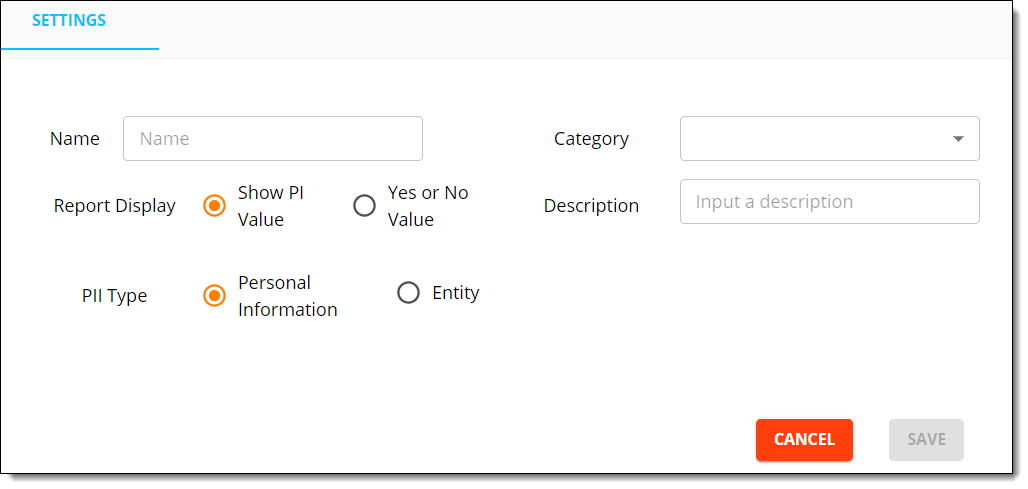
- Click Save.
- If you're only creating a tag, click Save and move on. Otherwise, proceed to Add regular expressions.
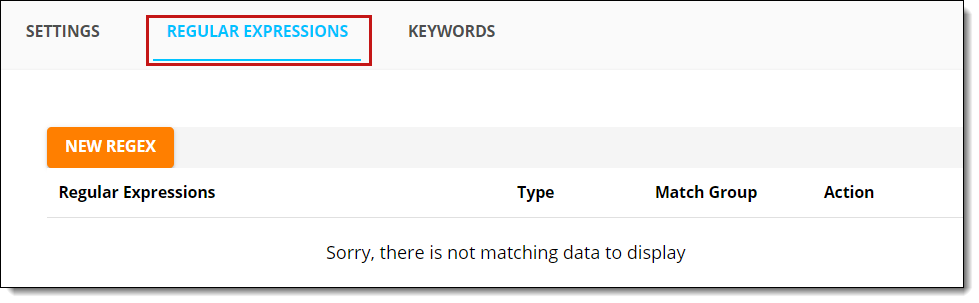
Add regular expressions
To add regular expressions to a new detector or tag:
- After saving your new detector or tag, open the Regular Expressions tab.
- Click New Regex.
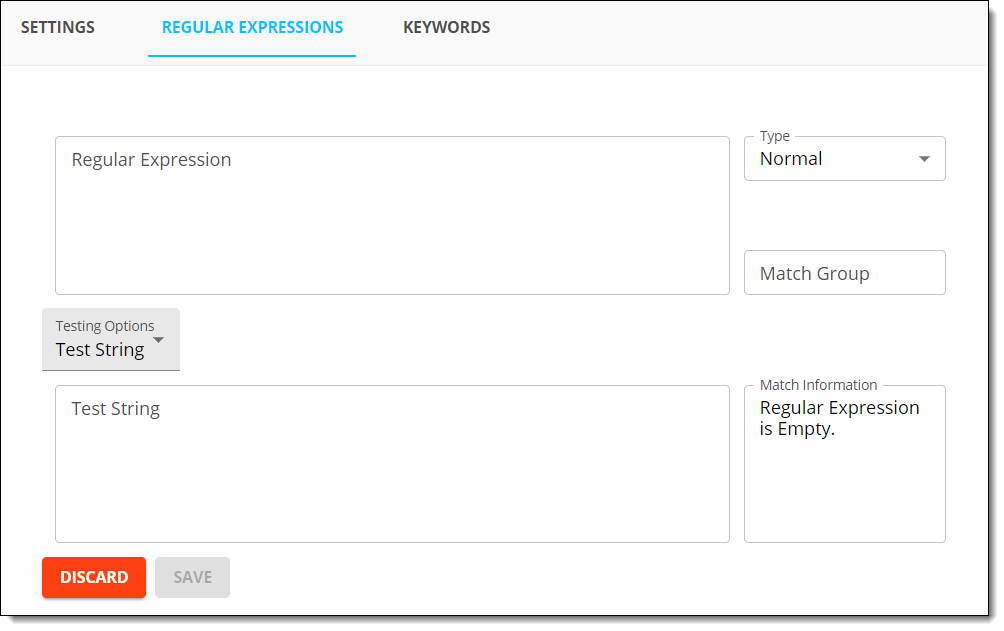
- Enter a regular expression in the Regular Expression text box.
- For more information on regular expressions, see Frequently asked questions.
- Select a Type for the regular expression.
- Normal— Normal regex patterns are designed to match PI within text. Any PI matches are filtered by the machine learning model (if one exists) and successful matches returned as PI.
- Bypass model— It is sometimes convenient to bypass the machine learning model, if it is certain that the regex is targeted enough to capture PI.
For example, it’s very likely that the text following “BIC code” is in fact a BIC code, so the following regex pattern can be specified to capture this:\bbic\s*(code\s*){0,1}:*\s+\b([A-Z]{6}[\dA-Z]{2}(?:[\dA-Z]{3})?)\b.
This regex matches PI like “Bic code: ABCDEF” and is not passed to a machine learning model for additional filtering. - Blocklist— A blocklist regex can be used to specify negative patterns for PI. For example, for an SSN detector, it may be beneficial to specify that placeholder social security numbers like 000-00-000 should not be returned.
- Specify a Match Group for the regular expression, if necessary.
- Match group indicates which matching group contains the PI.
For example, take the following regular expression:(ssn|social security number)\s*+:\s*+(\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}).
This regular expression matches two groups, (ssn|social security number), and (\d{3}-\d{2}-\d{4}), but only group 2 contains the personal information to be captured. Therefore, the match group would be set to 2.
- Match group indicates which matching group contains the PI.
- Test the regular expression. For more information on how to test regExes and keywords, see Testing RegExes and keywords.
- Click Save.
- Repeat steps 5-8 as necessary.There is no limit to how many regExes,of any type,that can be specified for a detector.
Add keywords
To add keywords to a detector or tag:
- Navigate to the Keywords tab and click New Keyword.
- Enter a keyword in the Keyword text box.

- Specify a Type for the keyword:
- Global Keyword— A global keyword term is a term that must appear somewhere in the body of the document. If a global keyword is not found in the document, the detector will not return PI matches.
- Global Blocklist Keyword— A global blocklist term is a term that must not appear anywhere in the body of the document. If a global blocklist term is found in the document, the detector will not return any PI matches.
- Local Keyword— A local keyword term is a term that must appear near a PI matched via a regex pattern. You can specify a maximum distance in characters to indicate how far away the term should be on either side of the PI found. If the term is not found within the specified distance, the detector will not return that PI match.
- Local Blocklist Keyword— A local blocklist term is a term that must not appear in the vicinity of a PI match. You can specify a maximum distance. If the local blocklist term appears within that distance of a PI match, the PI match will not be returned.
- If you select a Local Keyword or a Local Blocklist Keyword, specify a Max Keyword Distance.
- The Max Keyword Distance dictates how far away a keyword is permitted to be on either side of information found by a regular expression.
- The default value is 40 characters.
- Test the keyword. For more information on how to test regExes and keywords, see Testing RegExes and keywords.
- Click Save.
- Repeat steps 1-6 as needed.
Save the detector
To save a detector:
- Navigate to the Settings tab for the detector. Click Save.For updates to a detector to be incorporated the next time you run Data Analysis, the entire detector must be saved.
- If the detector was just created, click Save and Build.
Testing RegExes and keywords
Before adding a new regular expression or keyword to a detector, or while editing an existing one, you can test the regex or keyword using a test string.
To test a regEx or keyword:
- After adding or editing a detector, select Test String from the Testing Options drop down.
- Copy and paste a test string containing the information to capture.
- Test information that should not be captured to be sure that the regEx or keyword is only capturing intended information.
- The Match Information box will display the result.
- No matches found if the regEx/keyword did not pick up the information or
- Detected PI 0: [information that has been detected] if there is a match.
Frequently asked questions
RegEx is a string of characters that represents a pattern. You can use RegEx to search for text that matches these patterns. For example, to detect Employee ID’s that consist of 2 capital letters followed by 5 digits, you could create the following custom detector using the expression: \b([A-Z]{2}[\d]{5})\b
Where:
- \b represents a word boundary
- [A-Z]{2} represents two capitalized letters in the range A to Z
- [\d]{5} represents 5 digits
- The parentheses ( ) are put around the token we want to capture as the ID
Example scenario
For a particular project, it may be important to identify Employee ID’s. Employee ID is not an out of the box detector, so building a custom detector is required.
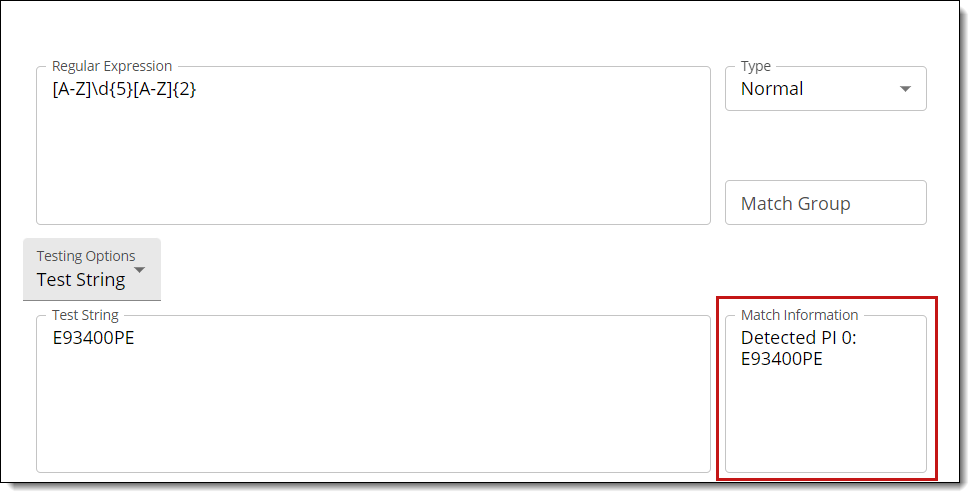
Employee ID’s look like the following:
- N68020KL
- E93400PE
In other words, they are all in the form of one capital letter followed by 5 digits, followed by two more capital letters.
Then, the corresponding regex would be: [A-Z]\d{5}[A-Z]{2}
Following the steps described in “Testing RegExes and Keywords,” you can use the interface to test whether this regex works:
In the box in the bottom right-hand corner, the text says:
- Detected PI 0:
- N68020KL
This indicates that the regex successfully recognizes Employee ID’s.
RegEx recommendations
- Avoid the * character when creating regexes, as they can result in performance issues.
- Data Breach Response uses the Java 8 version of regexes.