You can create a repeated content filter or a regular expression filter on the Repeated Content Filters tab in order to improve the quality of an Analytics index. Using a structured analytics set, you can allow Relativity to automatically create repeated content filters by running the repeated content identification operation on a set of documents. See Creating a structured analytics set for steps to create a structured analytics set with Repeated content identification.
A repeated content filter finds the text wherever it occurs in each document that matches your configuration parameters and suppresses it from the Analytics index. We recommended using this filter to ensure that the authored content of a document isn't overshadowed by content such as confidentiality footers or standard boilerplates. If included in an Analytics index, disclaimers and other repeated content can create false positive relationships between documents.
A regular expression (RegEx) filter removes any text that matches a specified regular expression. This custom filter may be used if there are repeated segments of text with slight variations throughout the data set, such as Bates numbers. The filter may be used on Analytics indexes or structured analytics sets. To learn more about RegEx, see Searching with regular expressions (regex).
You can link multiple filters to your analytics index, but you should not exceed 1,000 repeated content filters on an index. Filters do not affect the original data in Relativity; they only apply to the indexed data.
See this related page:
Creating a repeated content filter
You may create repeated content filters manually, or you may use Repeated Content Identification which will create the filters for you. To create a repeated content filter manually, use the following steps:
- Click the Indexing & Analytics tab followed by Repeated Content Filters.
- Click New Repeated Content Filter. The Repeated Content Filter layout displays.
- Complete the fields on the Repeated Content Filter layout to create a new filter. See Fields. Fields in orange are required.
- Name - the name of the filter.
- Type - type of repeated content filter. Select one of the following options:
- Regular Expression - filters out text defined by the regular expression you specify in the Configuration field. This filter uses the regular expression syntax supported by the java.util.regex.Pattern Java class, which is very similar to Perl regular expressions.
- Repeated Content- filters out text that matches the phrase specified in the Configuration field.
Regular expression filters may be applied to either Analytics indexes or structured analytics sets (via the structured analytics set page). However, only one regular expression filter may be linked to a structured analytics set. If multiple regular expressions are needed for a given structured analytics set, the regular expression needs to be written in order to satisfy all conditions.
The following table provides examples of regular expressions for specific types of content:
Regular expression Content type \b(?:http|https|mailto)://\S{1,1024}\b URLs \bREL_[0-9]{8}\b Bates-style ID such as REL_12345678 \S{1,100}@\S{1,100} Email addresses (?i)(Von.*?Gesendet.*?An.*?Cc:.*?Betreff.*?\r\n)
Note: The regular expression flag (?i) forces a case insensitive match. This is necessary because matching for what to filter out from Structured Analytics analysis is case-sensitive.
Non-English languages (e.g., a German email header)
Von: John Smith
Gesendet: Mittwoch, 26 August 2015 17:05
An: Simon, Jane
Cc: Johnson, Ed
Betreff: Hallo
Repeated content filters may be applied to Analytics Indexes. These will not affect structured analytics sets. They can't be used for other index types, such as dtSearch.
- Configuration - string or value defining the repeated content or regular expression to be removed by this filter. The matching text will be suppressed from the Analytics Index or structured analytics set, but the text in Relativity will remain untouched.
- Ready to index - administrative field used to find repeated content filters in a list based on Yes or No values. When evaluating repeated content filters, you can select Yes to designate that the filter should be linked to an Analytics index. Please note that this field is not required in order to add a filter to an Analytics index.
- Number of occurrences - numeric field that shows the total number of documents containing the Configuration text. Relativity updates this field after running a structured analytics set with the Repeated content identification operation. A higher number of occurrences indicates the filter would have more impact on the conceptual space. For more information on how these are set, see Creating a structured analytics set.
- Word count - numeric field that shows the word count of the Configuration text. Relativity updates this field after running a structured analytics set with the Repeated content identification operation. A higher word count indicates the filter would have more impact on the conceptual space. For more information on how these are set, see Creating a structured analytics set.
- Click Save to save the filter.
-
You may optionally add the filter to an Analytics index or a structured analytics set:
-
For an Analytics index, tag the filter as “Ready to index,” then link it to the index. See Linking repeated content filters to a conceptual index.
-
If the filter is a regular expression, add it to a structured analytics set by selecting the regular expression under the Regular expression filter field on the structured analytics set.
Note: Tagging a regular expression filter as "Ready to index" does not automatically add it to a structured analytics set.
-
Fields
The Repeated Content Filter layout and default tab view contain the following fields:
Evaluating repeated content identification results
After running the repeated content identification operation using a structured analytics set, verify that the configuration settings were able to capture meaningful repeated content. If not, you need to adjust the operation settings appropriately and re-run the operation.
We recommend evaluating the filters created by Repeated content identification before linking to an Analytics index.
Use the following steps to evaluate repeated content identification results:
- Click the Indexing & Analytics tab, followed by the Structured Analytics Set tab.
- Click the name of a structured analytics set you ran with the Repeated content identification operation.
- Click View Repeated Content Filter Results on the Structured Analytics Set console. This opens the Repeated Content Filters tab with a search condition applied to view repeated content filters related to the selected structured analytics set.
- Review the text of the Configuration field for filters with a high number of occurrences and high number of words. These help the index the most. Evaluate these filters as a priority. If there appears to be authored content in the Configuration field, don't use the filter. If the text appears to be an email signature or email header, it is unnecessary to use the filter as this data is handled by the email header filter or the automatically remove English signatures and footers feature. Capitalization does not matter.
- Select the filters that you want to apply to your index.
- Select Checked and Edit, and then click Go on the mass operations bar.
- Select Yes for the Ready to index field, and then click Save to tag the selected filters as ready to index.
- Repeat steps 4-8, but filter or sort on the Word Count field. Filters with a high word count help the index the most. Evaluate these filters as a priority.
Note: If the text in the Configuration field appears to be cut off, consider increasing the maximum number of words value and running the repeated content identification operation again. Filtering the entirety of the repeated text may improve performance.
Note: This step is optional. The Ready to Index field helps simplify managing a large number of filters.
After you finish evaluating the repeated content filters, consider using the Mass Delete operation on the mass operations bar to remove any filters you don't plan to use.
Once you determine the repeated content filters you want to use, link them to an Analytics index. See Linking repeated content filters to a conceptual index for instructions on how to link repeated content filters.
Repeated content filters naming convention
For each repeated content filter created by a structured analytics set with the repeated content filter operation, the Name column contains the following information:
- Structured analytics set prefix - the prefix entered for the structured analytics set used to run the repeated content identification operation.
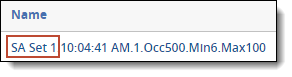
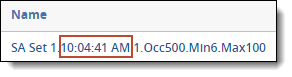
- Timestamp - the timestamp (HH:MM:SS AM/PM) for the operation run.
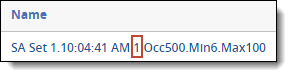
- Identifier - the auto-generated identifier for the repeated content. The identifier values are assigned incrementally to an ordered list of patterns. This list is sorted by a decreasing product value (word count multiplied by the number of occurrences).
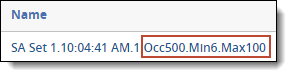
- Operation settings - the minimum number of occurrences (Occ#), minimum number of words (Min#), and maximum number of words (Max#) settings.