Service Host Manager
Relativity services defined within the Relativity.Services application and other applications, such as
Productions example
The following diagram illustrates how the Service Host Manager is used by Relativity productions:
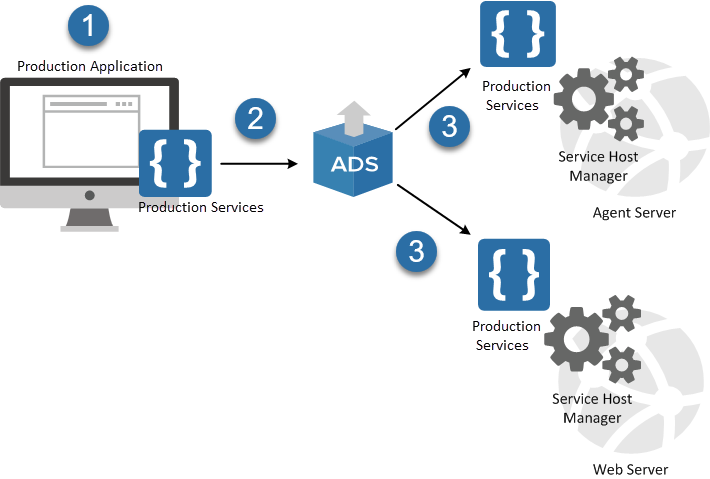
- Production is a Relativity application installed by default.
- When you install Relativity, the Production application is deployed using the Application Deployment System (ADS).
- As part of the application installation, the ADS deploys the services included in the Production application to all web and agent servers in your environment. These services are run by the Service Host Manager.
When you use Relativity productions, the browser user interface calls the services, for example, to create, update, or run productions. If the Service Host Manager is down, you can't interact with productions.
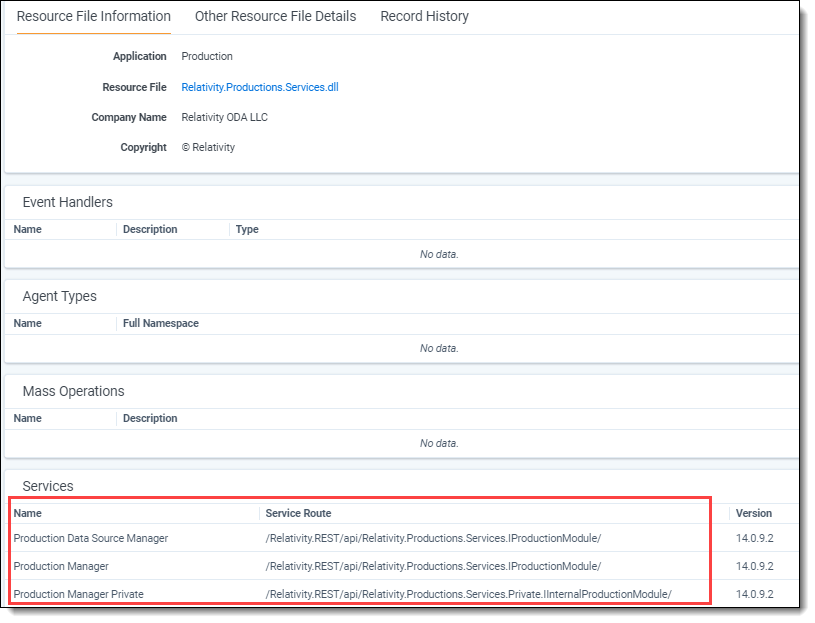
You can view the services associated with a Relativity application using the Resource Files tab. The following example displays the services in the Relativity.Productions.Services.dll.
Identifying a process running a specific service
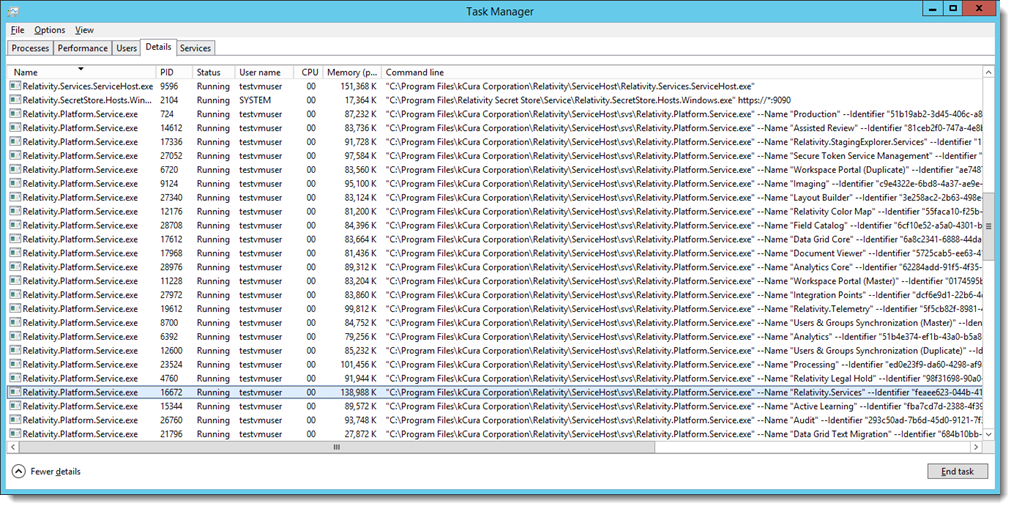
The services running in the Service Host Manager are hosted as individual processes. Each of these services execute as a separate instance of Relativity.Platform.Service.exe, resulting in improved stability, and greater ease in identifying services that have failed. To minimize downtime experienced by Relativity users, the Service Host Manager now attempts to restart a failed service up to three times, rather than require a full restart of the service host.
To determine the application service running in a process, open the Task Manager, then select the Details tab, and view the Command line column. You may need to right-click on the column headings and then select the Command line column to display it.
You can prevent services from starting by listing them in the ServiceHostExclusionList instance setting. If you add a GUID for a service to this list while the Service Host is running, the service shuts down dynamically. Similarly, if you remove a GUID, the service starts dynamically. Do not suspend required services unless Customer Success or Relativity engineers advise you to do so.
Port configuration
In certain network environments, it may be necessary to customize port settings for the Service Host Manager:
- Service Host Manager by default runs on port 8995 (http://localhost:8995). If the port is not available on your system, add the ServiceHostServiceLocation instance setting with a different port value to explicitly specify the port to use.
- Name – ServiceHostServiceLocation
- Section - kCura.Service.ServiceHost
Value - specify the port number to use
- Individual service endpoints deployed with the Service Host are assigned port numbers from the default range of 10000–20000. To specify a different port number range, add the ServiceHostPortRange instance setting.
- Name – ServiceHostPortRange
- Section - kCura.Service.ServiceHost
- Value - specify the port ranges to use
The range value must be pipe-delimited (20000|30000). You can look up the port number assigned to a specific service in the EDDS.ApplicationServiceLocation table.
HTTPS configuration
Follow these steps to enable HTTPS for the Service Host Manager:
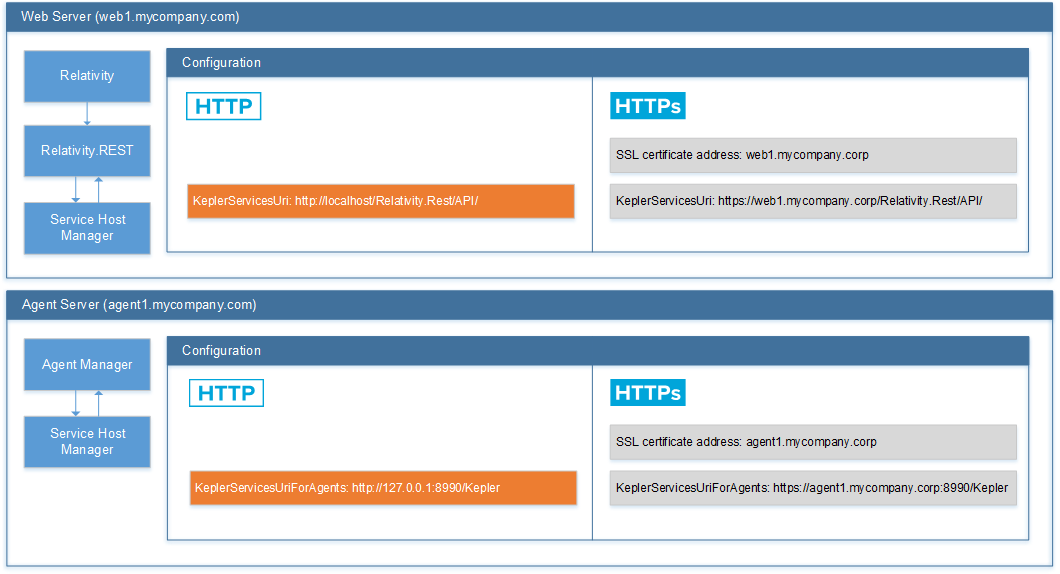
- Change the values of the KeplerServicesUri and KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance settings to HTTPS URIs for each server.
The values of KeplerServicesUri and KeplerServicesUriForAgents for HTTPS URIs must match the SSL certificate address, so they cannot use localhost or 127.0.0.1.
- Set up the certificate on each server:
- Install the certificate to the Personal certificate store for the Computer Account on all web and agent servers.
If the certificate is self-signed, you must add it to both the Personal and the Trusted Root Certification Authorities certificate stores for the Computer Account on all web and agent servers.
The certificate is bound to IP 0.0.0.0 on the machine hosting Service Host Manager (specified in the KeplerServicesUri instance setting), and the URI of the agents server (KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance setting). The port that the certificate is bound to is as follows:
- Service Host Manager – the port that the certificate is bound to is determined when the service is started by iterating through the ports specified in the ServiceHostPortRange instance setting (default is 10000 – 20000, as described above). For example, for productions services the certificate may be bound to port 10001 and processing services to port 10002.
- Agents URI – the certificate is bound to the port specified in the URI in the KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance setting. For example, https://agent1.mycompany.corp:8990 binds the certificate to port 8990.
The host name specified in the KeplerServicesUri and KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance settings for each web and agent server must match the host name (“Issued To” value) of the certificate. For example, if the agents server host name is https://rel-agent-server1, the KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance setting must be https://rel-agent-server1:8990/Kepler.
- Upon initialization, Service Host and the Agent Manager attempt to automatically configure HTTPS and select the certificate (because KeplerServicesUri and KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance settings include the HTTPS prefix). Certificate selection logic is as follows:
- Open the Personal store for the Computer Account and look for an exact host name match. The host name comes from the KeplerServicesUri and KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance settings.
- If there is no exact host name match, query the store for all valid certificates and use the one with the largest encryption key.
- If there are no valid certificates, look for a wildcard certificate that would work.
- If there are no valid wildcard certificates and the scheme is set to HTTPS, an exception is logged.
- To override the default automatic certificate selection behavior, add the SslCertificateThumbprint instance setting for the server to explicitly specify the certificate to use:
- Name – SslCertificateThumbprint.
- Section – kCura.Service.ServiceHost.
- Value – The thumbprint of the certificate for SSL bindings. For instructions on retrieving the thumbprint, see https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms734695(v=vs.110).aspx.
Make sure that you copy the Thumbprint certificate field when retrieving the thumbprint value (it's easy to confuse with the Serial number field). The thumbprint value must not include spaces (when you copy-paste it from the Windows certificate form, it does includes spaces). You must also remove the leading space because it contains an illegal character that can't be matched when the certificate is retrieved from the store. You likely have different certificates for different machines. To configure the certificate for HTTPS bindings for each machine, use the MachineName field of the instance setting.
- Install the certificate to the Personal certificate store for the Computer Account on all web and agent servers.
- Set the value of the EnforceHttps instance setting as necessary:
- EnforceHttps ensures that your KeplerServicesUri and KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance settings are set to HTTPS. If you have EnforceHttps set to On and your Kepler Uris are not set accordingly, Service Host will fail to host your services.
- EnforceHttps can ensure that all incoming Service Host Manager traffic uses HTTPS. If any request comes in as HTTP and EnforceHttps is set to On, Service Host will not accept the request. Setting EnforceHttps to Off does not force traffic to use HTTPS and allows HTTP. Setting EnforceHttps to Warn will still allow your services to be stood up as HTTP, but will log a warning.
Removing certificate bindings
Relativity unbinds certificates from ports as part of the services normal shutdown cycle. Because abnormal shutdowns can also occur, and Service Host Manager uses a range of ports, it is possible that over time all ports in the range may be bound to certificates. Removing bindings for server maintenance one-by-one can be time-consuming, so the recommended way of clearing them is by using command line. You must shut down Service Host Manager before running this command:
Relativity.Services.ServiceHost.exe --unbindports
HTTPS setup for dtSearch service
The dtSearch service is a self-hosted webservice that runs on any agent server on which the dtSearch Search Manager agent is enabled. Like Service Host, this service is not TLS-encrypted out of the box, but you now have the ability to enable this feature beginning in Server 2022.
To enable HTTPS on the dtSearch service, perform the following steps:
-
Fully configure Service Host for HTTPS, per the HTTPS configuration steps above.
-
Set the EnforceHttps instance setting to On. This instance setting can only be set to On if the Service Host has been fully configured for HTTPS.
-
Install a valid SSL Certificate. We recommend re-using the same certificate used to secure ServiceHost on each agent machine. This is possible because, like Service Host, the agent hostname is used in the URI for all calls to the search service. To confirm this, you can review the KeplerServicesUriForAgents instance setting. If for any reason you are not using agent hostnames, this topic contains best practices for configuring a certificate for each agent by hostname.
-
Register the SSL certificate to the search service's port. The default port for the dtSearch Search Service is 6870, but this can be overridden via the SearchAgentServicePort instance setting. Unlike Service Host, the search service will not auto-register your certificate on startup. This must be carried out by a server administrator or via automation of your own.
-
Enable HTTPS for the search service via the toggle kCura.EDDS.Agents.Toggles.EnableHttpsDTSearchToggle. This Relativity toggle, once enabled, will cause the search service to automatically switch to the HTTPS protocol. No manual restart is required.
Troubleshooting hosted services
If an application error indicates that a service did not deploy successfully, start by reviewing the information on the Errors tab. If you are unable to identify the cause on the Errors tab, review the Relativity log. For more information, see Logging.
In most cases, Service Host Manager errors are resolved when the service restarts. Once the Service Host Manager restarts, a new end point is generated and service is redeployed.
If the problems persist, review the Service Host Manager port and HTTPS settings described above.