Repeated content identification setup basics
This quick reference guide contains a basic workflow for setting up repeated content identification. For more detailed information, see Analytics.
Repeated content identification setup
The setup for running repeated content identification is comprised of two components:
- Saved search
- Structured analytics set
1. Saved Search Setup
Use the following conditions and fields to create the saved search used for email threading. You do not need to set a sort order on this search.
Search Name
Follow your team’s normal protocol for naming searches.
Conditions
The condition for this search can be the same as the conceptual index search if it is different than the conditions noted below.
- Extracted text size is greater than 0 KB.
- Extracted text size is less than 30 MB.
For workspaces with millions of documents, we recommend a sampling workflow. For more information, see Sampling for repeated content.
Fields
Any fields are acceptable.
2. Structured Analytics Set
Here are the steps and choices for creating a structured analytics set.
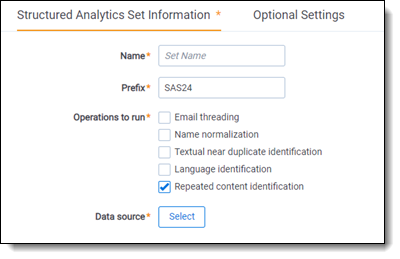
Structured Analytics Set Information
- Name—enter a name for the structured analytics set.
- Prefix—keep the default prefix or add your own prefix. Shorter prefixes, even just two characters, such as “LI,” take up less space in your views.
- Operations to run—select Repeated content identification.
- Data source—select the saved search you created above.
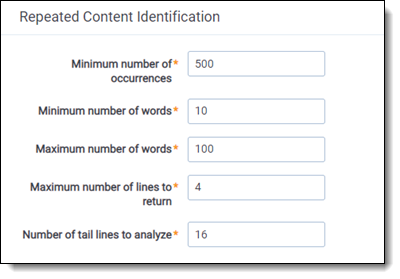
Repeated Content Identification
- Minimum number of occurrences—the minimum number of times a phrase must appear to be considered repeat content. We typically set this to .005 times the number of documents in your saved search.
- Minimum number of words—leave as default.
- Maximum number of words—leave as default.
- Maximum number of lines to return—leave as default.
- Number of tail lines to analyze—leave as default.
Optional Settings
Choose the appropriate Analytics server.







