Concept searching
You can use Concept searching to find information without a precisely phrased query by applying a block of text against the database to find documents that have similar conceptual content. This can help prioritize or find important documents.
Concept searching is very different from keyword or metadata search. A concept search performed in Analytics reveals conceptual matches between the query and the document quickly and efficiently, so you can focus on the concepts that you deem important. The following table illustrates the differences between standard searching and concept searching.
| Standard Method | Analytics Method |
|---|---|
|
Finds the presence (or absence) of a query (term or block of text) |
Derives the potential meaning of a query |
|
Simply looks for matches of query and indexed docs |
Attempts to understand semantic meaning and context of terms |
| Incorporates Boolean logic |
Incorporates mathematics |
With standard Keyword Search, people frequently experience “term mismatch,” where they use different terms to describe the same thing.
- “Phillipines” and “Philippines”—misspelling
- “Jive” and “jibe”—misuse of the word
- “Student” and “pupil”—synonyms
- “Pop” and “soda”— regional variation
Using concept searching, you can submit a query that is anywhere between a sentence to an entire document's length and return documents that contain the concept the query expresses. Using a single word for a query is not recommended as the results can be broad and unreliable. The match isn't based on any one specific term in the query or the document. The query and document may share terms, or they may not, but they share conceptual meaning.
Every term in a conceptual index has a position vector in the concept space. Every searchable document also has a vector in the concept space. These vectors, when close together, share a correlation or conceptual relationship. Increased distance indicates a decrease in correlation or shared conceptuality. Two items that are close together share conceptuality, regardless of any specific shared terms.
During concept searching, you create text that illustrates a single concept (called the concept query), and then submit it to the index for temporary mapping into the concept space. The conceptual analytics index uses the same mapping logic to position the query into the concept space as with the searchable documents.
Once the position of the query is established, the Analytics index locates documents that are close to it and returns those as conceptual matches. The document that is closest to the query is returned with the highest conceptual score. This indicates distance from the query, not percentage of relevancy—a higher score means the document is closer to the query, thus it is more conceptually related.
You can use concept searches in conjunction with keyword searches or dtSearches. Since a keyword can have multiple meanings, you can use a concept search to limit keyword search or dtSearch results by returning only documents that contain the keyword used in similar conceptual contexts.
Benefits of concept searching
The following are benefits of concept searching:
- Language contains many obstacles that prevent keyword search from being effective. These issues revolve around term mismatch—in that a single word can have many meanings (e.g., mean), multiple words can have the same meaning (e.g., “cold” and “frigid”), and some words have specialized meaning within a certain context or group of people. Concept search is more accurate and circumvents these issues because it does not depend upon term matching to find relevant documents.
- Communications can often be intentionally distorted or obfuscated. However, because concept search can see a document holistically, it can still find conceptual meaning in a document with intentional obfuscation.
- Concept searching forces the focus on conceptual relevancy rather than on any single term.
- Concept searching encourages the user to express a concept in the way that people are used to describing ideas and concepts. Concept searching can handle very long queries.
- Concept searching ultimately functions by finding term correlations within a document and across a document set. Therefore, in the context of the data set, Conceptual Analytics can provide a very accurate term correlation list (dynamic synonym list).
Special considerations
Note the following special considerations about running conceptual analytics operations:
- The following security permissions are required to run the operations:
Object Security Tab Visibility - Document - View
- Analytics Index - View
- Analytics Categorization Set - View, Edit, Add
- Analytics Categorization Category - View, Edit, Add
- Analytics Example - View, Edit, Add
Documents - In order to run an operation from the viewer, the document must be in the data set of an active Analytics index.
- You can only run operations in the Native Viewer and Extracted Text Viewer.
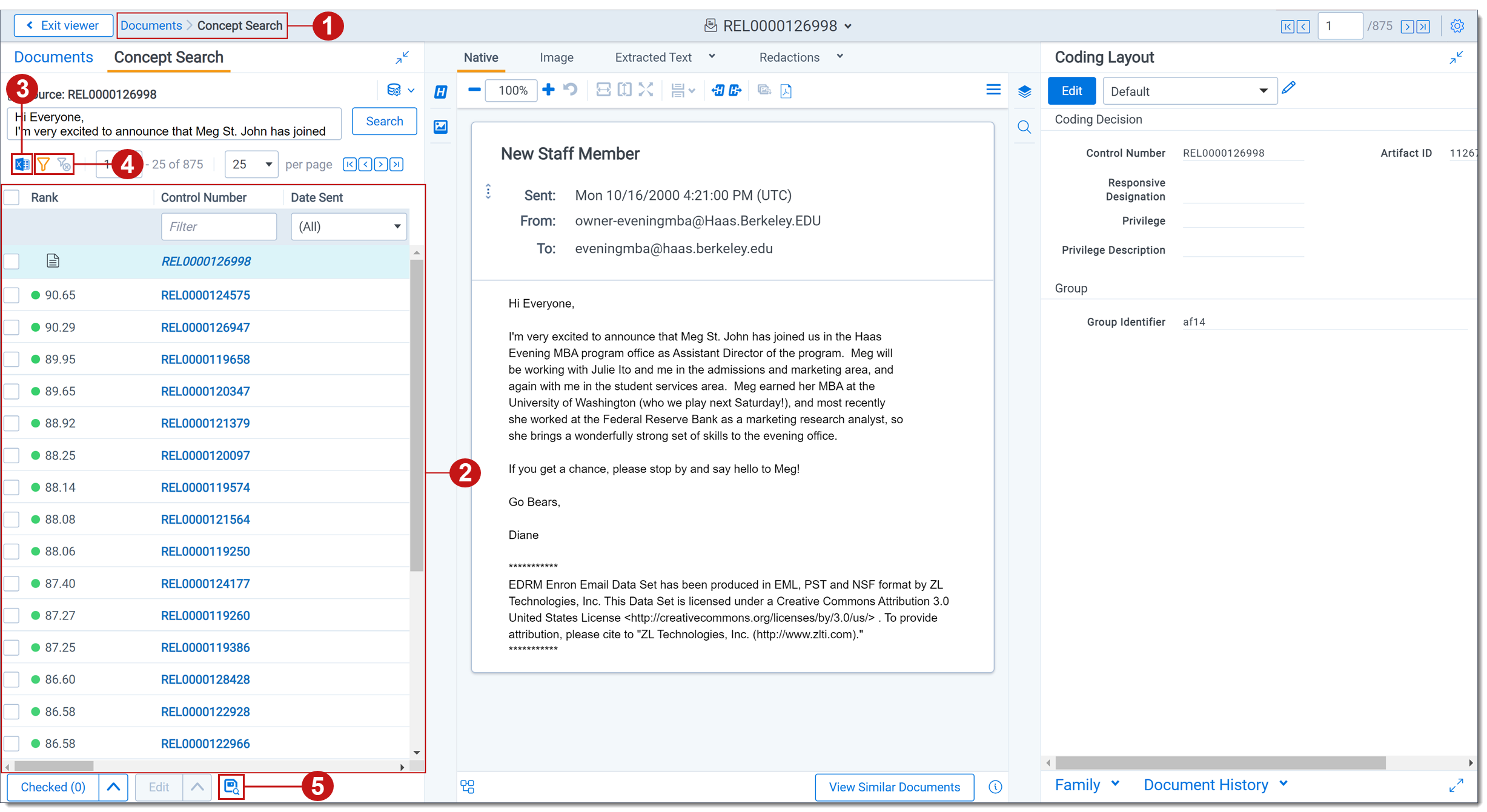
Running a concept search from the viewer
To run a concept search from the viewer, perform the following steps:
- Select a document from the document list, and then open it in the Native Viewer or Extracted Text Viewer. This is your primary document.
- Select a section of text, and then right-click the text.
- Select Concept Search from the right-click menu.
Once the operation is executed, the Documents list pane opens and displays the Concept Search tab, which contains documents that contain the concept the query expresses. This tab contains the following information about the results:
- Rank - the conceptual similarity of the document to the primary document. The higher the rank, the higher the relevance to the query. A rank of 100 represents the closest possible distance. The rank doesn't indicate the percentage of shared terms or the percentage of the document that isn't relevant.
- Control Number - the control number of the document.
The search text is automatically added to a textbox, which you can edit and then click Search to update your results.
The results are sorted by rank. The minimum concept rank used for the concept search is 60. This value isn't configurable.
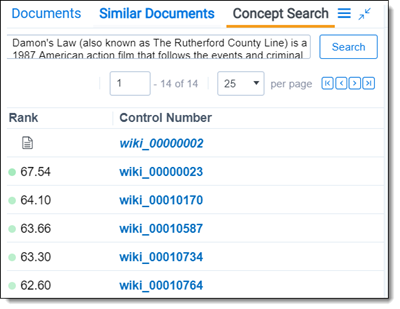
The rank measures the conceptual distance between the query text and the searchable documents in the conceptual index. The higher the rank, the higher the relevance to the query. A rank of 100 represents the closest possible distance. The rank doesn't indicate the percentage of shared terms or the percentage of the document that isn't relevant.
Navigating results
Once the conceptual analytics operation is executed, the following takes place:
Once the conceptual analytics operation is executed, the following takes place:
- The breadcrumb navigation includes Conceptual Analytics if you have run a concept search, find similar documents, or keyword expansion. If you navigate back to the Documents tab, this breadcrumb is removed.
- The Concept Search card updates to display the results of the operation and the number of documents returned by the operation.
- Optionally, you can click on the Filters icon to enable filtering. Enter the desired terms in a column and press Enter on your keyboard to filter the results.
- Optionally, click the Export to CSV icon to download a .csv file that contains the results in the Concept Search card.
- Optionally, to save the current documents in the Concept Search card as a saved search, do the following:
- Click the Save as Search icon in the bottom-left.
The Saved Search pop-up displays. - Enter the desired name in the Name field.
- Click Save.
- Click the Save as Search icon in the bottom-left.
If you have more than one active index, the Select Index icon displays in the upper-right of the card. The oldest active index (lowest Artifact ID) is chosen by default. To change indexes, click on the Select Index icon and select a different active index from the drop-down menu.
Running a concept search from the Documents tab
To run a concept search, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to the search panel.
- Click Add Condition.
- Select (Index Search) from the Add Condition drop-down menu.
- Select an conceptual analytics index.
- Perform one or more of the following tasks:
- In the Concepts box, enter a paragraph, document, or long phrase for a conceptual search.
Enter a block of text, rather than a single word to get better results. Single word entries return broad, unreliable results. A good example source might be a hot document from your workspace, a complaint for the case, or an excerpted paragraph from a relevant web article.
- Select any of these optional settings to control how your results are displayed:
- Select Sort by rank to order the documents in the result set by relevance. The most relevant documents are displayed at the top of the list.
- Select Min rank to set the ranking for a minimum level of conceptual correlation. The resulting set contains only documents that meet this minimum correlation level.
- Click Apply.
The (Index Search) window opens.
To stop a long running search, click Cancel Request.